b oxidation of odd chain fatty acids|A review of odd : Baguio Fatty acids with an odd number of carbons are found in the lipids of plants and some marine organisms. Many ruminant animals form a large amount of 3-carbon propionate during the fermentation of carbohydrates in the rumen. Long-chain fatty acids with an odd number of carbon atoms are found particularly in ruminant fat and milk. SW418 Sabong Live Review SW418 was once an extremely popular platform for e-sabong in the Philippines, with it offering HD live streaming services that are accessible even through mobile devices. Today, the site is non-functional and many review pages redirect visitors to other platforms unrelated to the original platform.
b oxidation of odd chain fatty acids,Oxidation of Odd-Chain Fatty Acids. Though most fatty acids of biological origin have even numbers of carbons, not all of them do. Oxidation of fatty acids with odd numbers of carbons ultimately produces an intermediate with three carbons called .To describe the reactions needed to completely oxidize a fatty acid to carbon .
The peroxisome degrades fatty acids that can't be oxidized in the mitochondria. .
To describe the reactions needed to completely oxidize a fatty acid to carbon dioxide and water. Like glucose, the fatty acids .
Fatty acids with an odd number of carbons are found in the lipids of plants and some marine organisms. Many ruminant animals form a large amount of 3-carbon propionate during the fermentation of carbohydrates in the rumen. Long-chain fatty acids with an odd number of carbon atoms are found particularly in ruminant fat and milk.

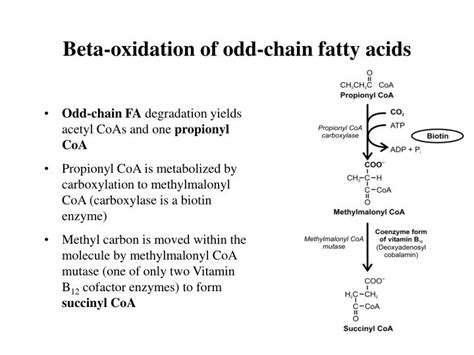
Oxidation of fatty acids occurs in multiple regions of the cell within the human body; the mitochondria, in which only beta-oxidation occurs; the peroxisome, where alpha- and beta-oxidation occur; and .Fatty acids with an odd number of carbon atoms are oxidized by the pathway of β-oxidation, producing acetyl-CoA, until a three-carbon (propionyl-CoA) residue remains. The 3- Carbon Propinyl co A is utilized .b oxidation of odd chain fatty acids One possible mechanism for the endogenous production of OCS-FAs is α-oxidation, involving the activation, then hydroxylation of the α-carbon, followed by the . The peroxisome degrades fatty acids that can't be oxidized in the mitochondria. These include very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) like 24:0 and 26:0, and in addition, branched-chain fatty acids .
Fatty acid β-oxidation is a multistep process by which fatty acids are broken down by various tissues to produce energy. Fatty acids primarily enter a cell via fatty acid protein . One possible mechanism for the endogenous production of OCS-FAs is α-oxidation, involving the activation, then hydroxylation of the α-carbon, followed by the . Most fatty acids are oxidized in the mitochondria, where the oxidation reaction occurs at the beta-carbon of the acyl chain, as shown in Figure 17.2.1 17.2. 1. Figure 17.2.1 17.2. 1: α and β carbons of .Although the fatty acid oxidation scheme works neatly for even‐ numbered chain lengths, it can't work completely for fatty acids that contain an odd number of carbons. β‐oxidation of these compounds leads to propionyl‐CoA and acetyl‐CoA, rather than to two acetyl‐CoA at the final step. The propionyl‐CoA is not a substrate for the TCA cycle or other simple . Oxidation of Odd-Chain Fatty Acids; Contributors and Attributions; Figure 6.11.1: Movement of Acyl-CoAs into the Mitochondrial Matrix. The process of fatty acid oxidation, called beta oxidation, is fairly simple. The reactions all occur between carbons 2 and 3 (with #1 being the one linked to the CoA) and sequentially include the following: A different pathway occurs for odd-length fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids. Beta oxidation of Saturated Fatty Acids with Even Carbon Chain Length Discussion. Once the fatty acids have been transported to the mitochondrial matrix via carnitine pathway, β-oxidation of fatty acyl-CoA (n carbons) occurs within the .The role of C17:0 and C15:0 in human health has recently been reinforced following a number of important biological and nutritional observations. Historically, odd chain saturated fatty acids (OCS-FAs) were used as internal standards in GC-MS methods of total fatty acids and LC-MS methods of intact . Donate here: http://www.aklectures.com/donate.phpsite video: http://www.aklectures.com/lecture/oxidation-of-odd-chain-fatty . The majority of research into fatty acid metabolism has been conducted primarily on even chain fatty acids (carbon chain length of 2–26) as these represent >99% of the total fatty acid plasma concentration in humans [11,12]. However there is also a detectable amount of odd-chain fatty acids in human tissue. Recent findings have shown a negative association between circulating odd chain fatty acids (OC-FAs); pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) and heptadecanoic acid (C17:0), with metabolic disease risk 1,2. .b oxidation of odd chain fatty acids A review of odd Generally, OCFAs are biosynthesized from odd-chain precursors (i.e., propionyl-CoA) or by α-oxidation-driven chain shortening of even-chain fatty acids. It has been found that branched-chain amino acids can contribute to the lipogenic propionyl-CoA pool (Crown et al. 2015 ) and that phytosphingosine could be metabolized to 15:0 . This document summarizes fatty acid oxidation through beta-oxidation. It discusses how fatty acids are broken down into acetyl-CoA in the mitochondria, generating energy in the form of ATP. Key points covered include the carnitine shuttle transport system, reactions of beta-oxidation, and oxidation of odd-chain and unsaturated fatty acids.Figure-3 -Beta oxidation of Linoleoyl co A (Dienoic acid- containing two double bonds) Regulation of fatty acid oxidation. There is regulation at the level of entry of fatty acids into the oxidative pathway by carnitine .
Explore the three major phases of oxidizing and extracting ATP from fatty acids within a cell. Dive into the activation process, understand the role of coenzyme A, and learn about the .Fatty acid 2-Hydroxylation in mammalian sphingolipid biology. Hiroko Hama, in Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids, 2010. Odd-chain fatty acids can be synthesized de novo by priming of fatty acid synthesis with propionyl-CoA instead of acetyl-CoA, which occurs at a negligible rate in most cells. Interestingly, early . Historical perspective. Georg Franz Knoop discovered fatty acid β-oxidation. In 1904, he published his classical experiments using odd and even chain ω-phenyl fatty acids such as ω-phenylvaleric acid and ω-phenylbutyric acid (Knoop 1904).Knoop fed these compounds to dogs and analysed their urine.
A review of oddb) β- oxidation of fatty acids is an extramitochondrial process. c) The enzymes present in the form of multienzyme complexes. d) The intermediates are carried by Acyl carrier protein. e) 129 ATPs are required for the formation of one mole of Palmitic acid. Q.16- β- oxidation of long-chain fatty acids occurs primarily in which of the following . In contrast, odd-chain saturated fatty acids (OCFAs), pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) and heptadecanoic acid (C17:0), represent only 1% and 0.5%, respectively, of fatty acids in whole fat milk 11.

Odd chain fatty acids (15:0 and 17:0) from dairy fat as well as odd chain phenolic lipids (alkylresorcinols) from whole grain are commonly reviewed as candidate biomarkers for dietary analysis and their ingestion are inversely related to chronic disease risks. Therefore, low levels of dietary intake of these odd chain molecules may be .
b oxidation of odd chain fatty acids|A review of odd
PH0 · Fatty Acid beta
PH1 · Biochemistry, Fatty Acid Oxidation
PH2 · Beta oxidation of odd chain and unsaturated fatty acids
PH3 · Beta oxidation of odd chain and unsaturated fatty
PH4 · Beta oxidation
PH5 · Beta Oxidation
PH6 · A review of odd
PH7 · A Review of Odd
PH8 · 9.4: Oxidation of Fatty Acids
PH9 · 6.11: Fatty Acid Oxidation
PH10 · 17.2: Oxidation of Fatty Acids